压铸成型
压铸件工艺就是把压铸金属、压铸模具和压铸机这三个压铸出产要素有机地组合和运用的过程。
压铸件工艺的原理是利用高压将金属液高速压入一精密金属模具型腔内,金属液在压力作用下冷却凝结而形成压铸件。冷、热室压铸是压铸工艺的两种基本方法。冷室压铸中金属液由手工或自动浇注设备浇入压室内,然后压射冲头前进,将金属液压入型腔。在热室压铸工艺中,压室垂直于坩埚内,金属液通过压室上的进料口自动流入压室。压射冲头向下运动,推动金属液通过鹅颈管进入型腔。金属液凝结后,压铸模具翻开,取出铸件,完成一个压铸循环。
What is Aluminum Die Casting ?
Hot chamber die casting can be used with aluminum, zinc, magnesium, and other low melting alloys using either our proprietary multi-slide or conventional tooling.
The hot chamber machine contains the melting pot, while the cold chamber melt pot is separate and the molten metal has to be ladled into the shot sleeve. With the internal mechanism, it makes the hot chamber the faster of the two processes. Other advantages of the hot chamber process include reduced porosity and longer die life from utilizing alloys that do not erode or dissolve the machine when put under heat or high pressure.
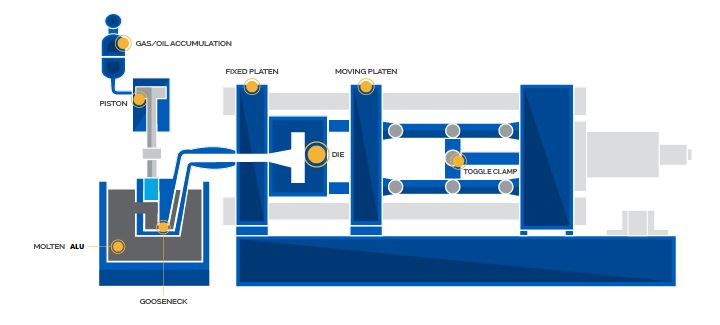
The injection mechanism of a hot chamber machine is immersed in the molten metal. The furnace is attached to the machine by a metal feed system called a gooseneck.
The die is closed and the piston rises, opening the port, allowing molten metal to fill the cylinder.
Next, the plunger seals the port, pushing the molten metal through the gooseneck and nozzle into the die cavity where it is held under pressure until it solidifies.
The die opens and the cores, if any, retract. The casting remains in only one die half – the ejector side. The plunger then returns, allowing residual molten metal to flow back through the nozzle and gooseneck.

Ejector pins push the casting out of the ejector die. As the plunger uncovers the filling hole, molten metal flows through the inlet to refill the gooseneck.





